Note
Click here to download the full example code
Fast Causal Inference (FCI) for causal discovery from observational data#
We will simulate some observational data and demonstrate how we will use the FCI algorithm.
# Authors: Adam Li <adam2392@gmail.com>
#
# License: BSD (3-clause)
import numpy as np
from causal_networkx import StructuralCausalModel
from causal_networkx.ci import GSquareCITest, Oracle
from causal_networkx.discovery import FCI
Simulate some data
# set a random seed to make example reproducible
seed = 12345
rng = np.random.RandomState(seed=seed)
# construct a causal graph that will result in
# x -> y <- z
func_uz = lambda: rng.binomial(n=1, p=0.25)
func_uxy = lambda: rng.binomial(n=1, p=0.4)
func_x = lambda u_xy: 2 * u_xy
func_y = lambda x, u_xy, z: x * u_xy + z
func_z = lambda u_z: u_z
# construct the SCM and the corresponding causal graph
scm = StructuralCausalModel(
exogenous={
"u_xy": func_uxy,
"u_z": func_uz,
},
endogenous={"x": func_x, "y": func_y, "z": func_z},
)
G = scm.get_causal_graph()
# sample the incomplete observational data
data = scm.sample(n=5000, include_latents=False)
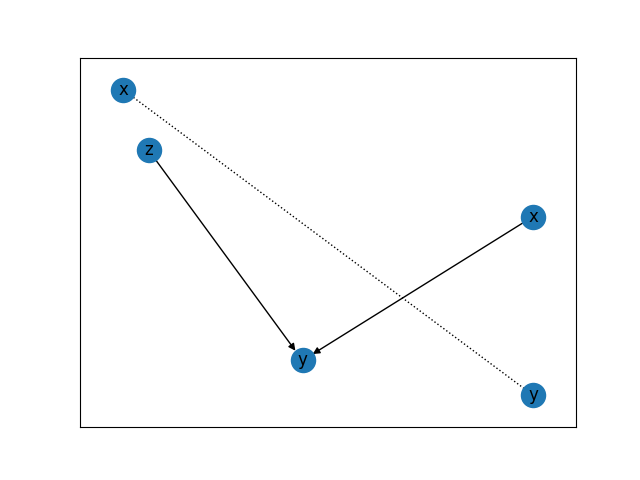
# note the graph shows a collider and will not show
# the unobserved confounder
G.draw()
Instantiate some conditional independence tests
oracle = Oracle(G)
ci_estimator = GSquareCITest(data_type="discrete")
Now we are ready to run the FCI algorithm.
fci = FCI(ci_estimator=ci_estimator)
fci.fit(data)
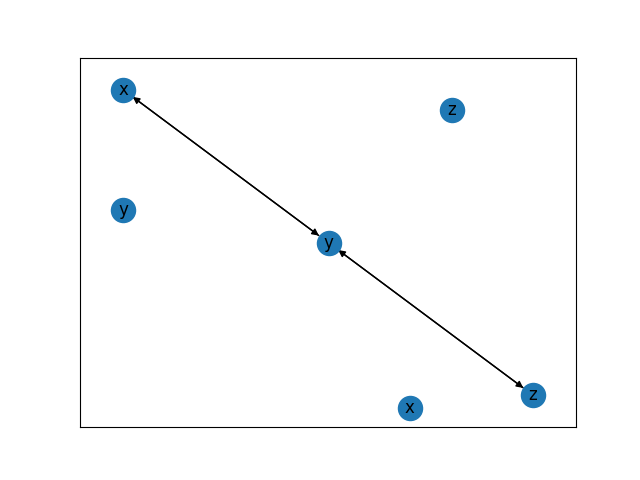
# the resulting partial ancestral graph (PAG) that is learned
graph = fci.graph_
graph.draw()
Out:
/home/circleci/project/causal_networkx/ci/g_test.py:199: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in divide
tlog[:, :, k] = contingency_tble[:, :, k] * nk[k] / tdijk
/home/circleci/project/causal_networkx/ci/g_test.py:201: RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in log
log_tlog = np.log(tlog)
/home/circleci/project/causal_networkx/ci/g_test.py:202: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in multiply
G2 = np.nansum(2 * contingency_tble * log_tlog)
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.027 seconds)